Capitalization, price volatility, continuation pattern
“Crypto Markets: Understanding Capitalisation, Price Volatility, and Continuation Patterns”
The world of cryptocurrency has been on a rollercoaster ride in recent years, with prices fluctuating wildly between highs and lows. As a result, investors have been forced to adapt their strategies to navigate the ever-changing landscape. In this article, we’ll delve into the key concepts of capitalisation, price volatility, and continuation patterns, providing insights into how these factors can impact cryptocurrency markets.
Capitalisation: A Key Indicator
Capitalisation refers to the total value of a company’s shares outstanding, divided by its market capitalization (market cap). In the context of cryptocurrency, capitalisation is particularly relevant, as it measures the perceived value of an asset. The higher the market capitalisation, the more valuable the asset is perceived to be.
A high-capitalisation cryptocurrency generally indicates strong demand from investors and institutional buyers. This can lead to a surge in price, as the market becomes increasingly optimistic about its potential for growth. Conversely, low-capitalisation cryptocurrencies may experience a decrease in value due to a lack of investor interest.
Price Volatility: The Unpredictable Nature of Cryptocurrency Markets
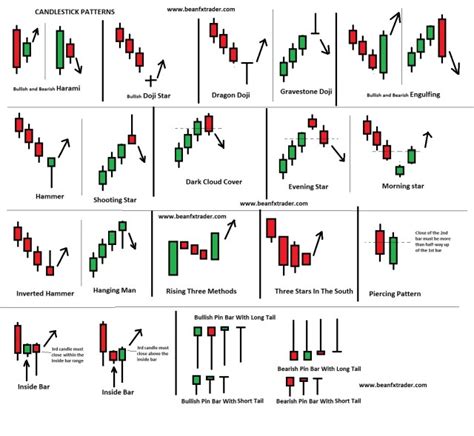
Price volatility is the primary characteristic that sets cryptocurrency markets apart from traditional assets. This unpredictability can be attributed to various factors, including:
- Market sentiment: Investor emotions and market trends can significantly impact price movements.
- Liquidity: Low trading volumes can lead to price swings due to a lack of buying and selling activity.
- Regulatory uncertainty: Changes in government policies or regulations can cause uncertainty and, subsequently, price volatility.
Cryptocurrency prices can fluctuate rapidly, often within seconds. This rapid price movement is known as “market making.” Market makers are entities that provide liquidity by buying and selling cryptocurrencies at prevailing market prices. When the market maker needs to sell a particular cryptocurrency, it can increase its bid price, causing the price to drop. Conversely, when the market maker wants to buy in, it can lower its offer price, leading to an increase.
Continuation Patterns: A Key Indicator of Price Movement
Continuation patterns are specific sequences of price movements that can be used as indicators to predict future price actions. These patterns can include:
- Ascending trends: Prices tend to rise after a downward trend.
- Descending trends: Prices tend to fall after an upward trend.
- Wedges: A combination of a rising and falling pattern, often accompanied by a sharp reversal.
To identify continuation patterns in cryptocurrency markets, traders need to observe the price chart over time. By analyzing charts from different periods, it’s possible to spot recurring patterns that can be used for prediction purposes.
Conclusion
Understanding capitalisation, price volatility, and continuation patterns is crucial for making informed investment decisions in the cryptocurrency market. By grasping these concepts, traders can better navigate the complex landscape of crypto markets and make more accurate predictions about future price movements.
As the cryptocurrency market continues to evolve, it’s essential to stay vigilant and adapt your strategies to accommodate changing market conditions. By combining knowledge of capitalisation, price volatility, and continuation patterns with technical analysis techniques, investors can increase their chances of success in this rapidly fluctuating asset class.